### Understanding Forbearance in Student Loans: What Does Forbearance Mean in Student Loans?
Guide or Summary:What is Forbearance?Types of ForbearanceHow to Apply for ForbearanceImplications of Forbearance on Student LoansAlternatives to Forbearance……
Guide or Summary:
- What is Forbearance?
- Types of Forbearance
- How to Apply for Forbearance
- Implications of Forbearance on Student Loans
- Alternatives to Forbearance
In the realm of student loans, many borrowers often find themselves in challenging financial situations, leading them to seek options that can ease their burden. One such option is forbearance. But what does forbearance mean in student loans? This term is crucial for students and graduates navigating their repayment journey, and understanding it can significantly impact their financial health.
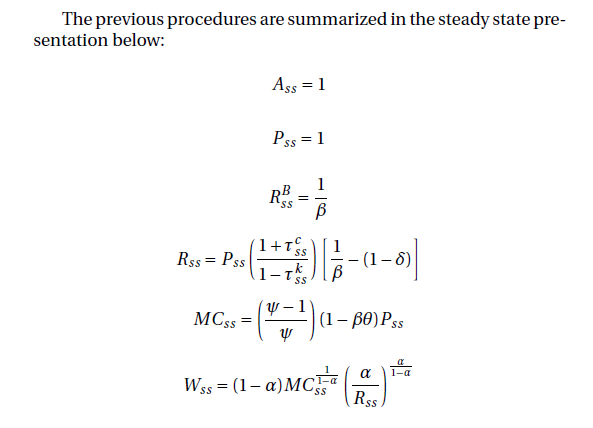
What is Forbearance?
Forbearance is a temporary relief option that allows borrowers to pause or reduce their student loan payments for a specified period. This can be particularly beneficial for those who are experiencing financial difficulties, such as job loss, medical emergencies, or other unforeseen circumstances. During forbearance, interest may continue to accrue on the loan, which can increase the total amount owed once the repayment period resumes.
Types of Forbearance
There are two primary types of forbearance: discretionary and mandatory. Discretionary forbearance is granted at the lender's discretion. Borrowers must provide a valid reason for their request, such as financial hardship or medical issues. On the other hand, mandatory forbearance must be granted by the lender if the borrower meets specific criteria set by federal regulations, such as serving in a medical or dental internship or residency.
How to Apply for Forbearance
To apply for forbearance, borrowers typically need to contact their loan servicer directly. The servicer will provide the necessary forms and information regarding the application process. It is essential for borrowers to communicate their financial situation clearly and to keep records of all correspondence. Additionally, borrowers should be aware of the timeline for approval and any potential impacts on their credit score.
Implications of Forbearance on Student Loans
While forbearance can provide immediate relief, it is important to understand its long-term implications. Since interest continues to accumulate during forbearance, borrowers may find themselves with a larger loan balance when they return to repayment. This can lead to higher monthly payments and increased total interest paid over the life of the loan. Therefore, it is crucial for borrowers to consider alternative options, such as income-driven repayment plans, which may offer more sustainable solutions.
Alternatives to Forbearance
Before opting for forbearance, borrowers should explore other alternatives. Income-driven repayment plans adjust monthly payments based on the borrower’s income and family size, potentially leading to lower payments that align with their financial situation. Additionally, deferment is another option that allows borrowers to temporarily stop making payments without accruing interest, provided they meet specific eligibility criteria.

In conclusion, understanding what forbearance means in student loans is essential for borrowers facing financial challenges. While it can offer temporary relief, it is crucial to weigh the pros and cons carefully. Borrowers should consider all available options, including income-driven repayment plans and deferment, to ensure they make informed decisions that will benefit their financial future. By taking the time to understand forbearance and its implications, students and graduates can navigate their repayment journey more effectively, ultimately leading to better financial outcomes.